


Next: Classical domes
Up: Telescope aerodynamics
Previous: Telescope aerodynamics
In a typical telescope the top ring with the spiders
(see fig.  ) represents the largest drag
contribution to the aerodynamic torque acting on the telescope.
Therefore
measurements of the flow characteristics near the upper
part of the telescope are representative of the overall aerodynamic
action which influences the guiding performance.
) represents the largest drag
contribution to the aerodynamic torque acting on the telescope.
Therefore
measurements of the flow characteristics near the upper
part of the telescope are representative of the overall aerodynamic
action which influences the guiding performance.
The guiding rms
error will depend on the amplitude of the torque
spectra about the two axes of the telescope -
equations ( ) and (
) and ( ).
Inserting equation (
).
Inserting equation ( ) in (
) in ( ) the torque
spectrum about any axis y can be expressed as:
) the torque
spectrum about any axis y can be expressed as:
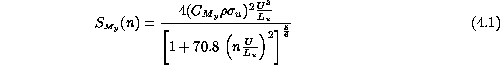
We see that 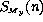 is a function of the static torque coefficient
is a function of the static torque coefficient 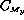 =
=
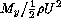 , and of
the three flow parameters:
, and of
the three flow parameters:
- U, mean speed
-
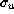 , speed rms
, speed rms
-
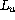 , turbulence length scale
, turbulence length scale
In the following sections, we present the results of
measurements of the parameters U, 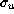 and
and 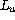 in various types of enclosures,
in the region of the upper part of the telescope:
in various types of enclosures,
in the region of the upper part of the telescope:
- [A]
- Measurements of wind turbulence in the dome of the ESO
3.6-m telescope.
- [B]
- Wind tunnel tests on a 1/50 model of the NTT enclosure.
- [C]
- Wind tunnel tests on a 1/64 model of the VLT
cylindrical enclosure.
- [D]
- Wind tunnel tests on a 1/80 model of the alternative
retractable enclosure for the VLT.
The measurements in the 3.6-m dome were performed by the author with
the help of F. Rigaut, who at the time was serving as a
cooperant at La Silla.
The wind tunnel studies were defined and coordinated by the author
and contracted by ESO to specialized laboratories equipped with a
boundary layer wind tunnel which allows a realistic simulation of the
wind turbulence.



Next: Classical domes
Up: Telescope aerodynamics
Previous: Telescope aerodynamics
Lorenzo Zago, lorenzo.zago@heig-vd.ch,
Mon Nov 6 23:33:14 GMT+0100 1995
 ) represents the largest drag
contribution to the aerodynamic torque acting on the telescope.
Therefore
measurements of the flow characteristics near the upper
part of the telescope are representative of the overall aerodynamic
action which influences the guiding performance.
) represents the largest drag
contribution to the aerodynamic torque acting on the telescope.
Therefore
measurements of the flow characteristics near the upper
part of the telescope are representative of the overall aerodynamic
action which influences the guiding performance.



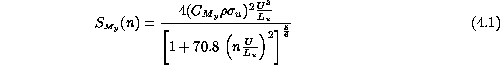
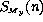 is a function of the static torque coefficient
is a function of the static torque coefficient 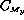 =
=
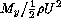 , and of
the three flow parameters:
, and of
the three flow parameters:
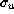 , speed rms
, speed rms
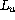 , turbulence length scale
, turbulence length scale
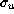 and
and 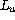 in various types of enclosures,
in the region of the upper part of the telescope:
in various types of enclosures,
in the region of the upper part of the telescope: