


Next: Analysis and modeling
Up: Experimental studies
Previous: Seeing tests on
[Barr] studied the mirror seeing of a 1.8-m
horizontal mirror in the range of mirror-air temperature
differences -1.5 K 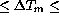 1.9 K
by analyzing interferograms of the front surface.
Unfortunately the large aberrations of the mirror and the change of
tilt and focus between and during the test runs limit exceedingly the
accuracy of the results and the comparison of different mirror conditions.
The researchers also intended to verify
the utility of small blowers placed around the mirror to create an
artificial airflow . However their power was too weak to create a
sustaining airflow capable to predominate the free convection flow
pattern.
1.9 K
by analyzing interferograms of the front surface.
Unfortunately the large aberrations of the mirror and the change of
tilt and focus between and during the test runs limit exceedingly the
accuracy of the results and the comparison of different mirror conditions.
The researchers also intended to verify
the utility of small blowers placed around the mirror to create an
artificial airflow . However their power was too weak to create a
sustaining airflow capable to predominate the free convection flow
pattern.
Possibly the most significant result of this work is the analysis
performed on the phase structure functions of the interferograms
which concluded that they follow well the form predicted for
Kolmogorov turbulence for separation distances up to 80 cm.
Since the largest temperature fluctuations are found at a much
shorter distance from the surface and are therefore associated to
small turbulence length scales, this result of [Barr]
makes admissible to use a 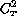 parameterization also in the case of
mirror seeing.
parameterization also in the case of
mirror seeing.



Next: Analysis and modeling
Up: Experimental studies
Previous: Seeing tests on
Lorenzo Zago, lorenzo.zago@heig-vd.ch,
Mon Nov 6 23:33:14 GMT+0100 1995
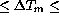 1.9 K
by analyzing interferograms of the front surface.
Unfortunately the large aberrations of the mirror and the change of
tilt and focus between and during the test runs limit exceedingly the
accuracy of the results and the comparison of different mirror conditions.
The researchers also intended to verify
the utility of small blowers placed around the mirror to create an
artificial airflow . However their power was too weak to create a
sustaining airflow capable to predominate the free convection flow
pattern.
1.9 K
by analyzing interferograms of the front surface.
Unfortunately the large aberrations of the mirror and the change of
tilt and focus between and during the test runs limit exceedingly the
accuracy of the results and the comparison of different mirror conditions.
The researchers also intended to verify
the utility of small blowers placed around the mirror to create an
artificial airflow . However their power was too weak to create a
sustaining airflow capable to predominate the free convection flow
pattern.



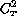 parameterization also in the case of
mirror seeing.
parameterization also in the case of
mirror seeing.